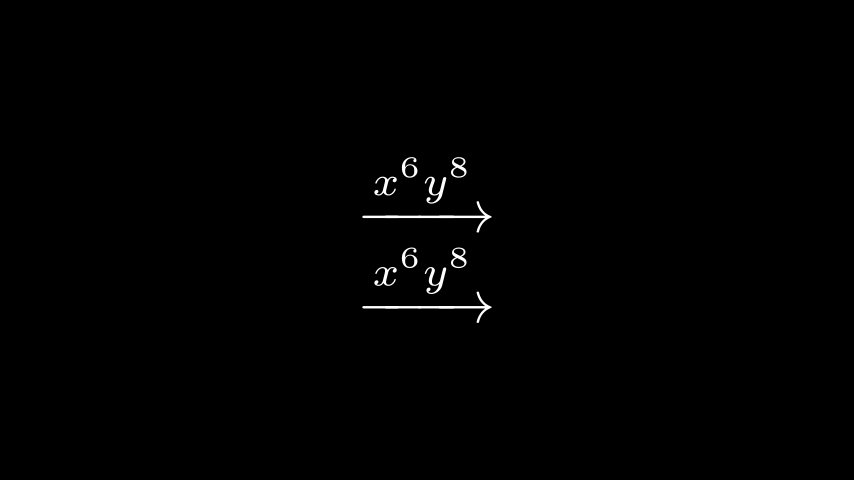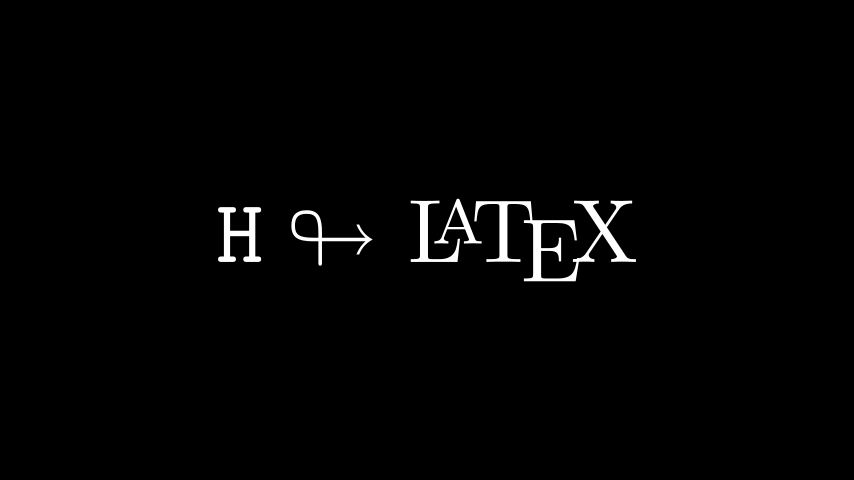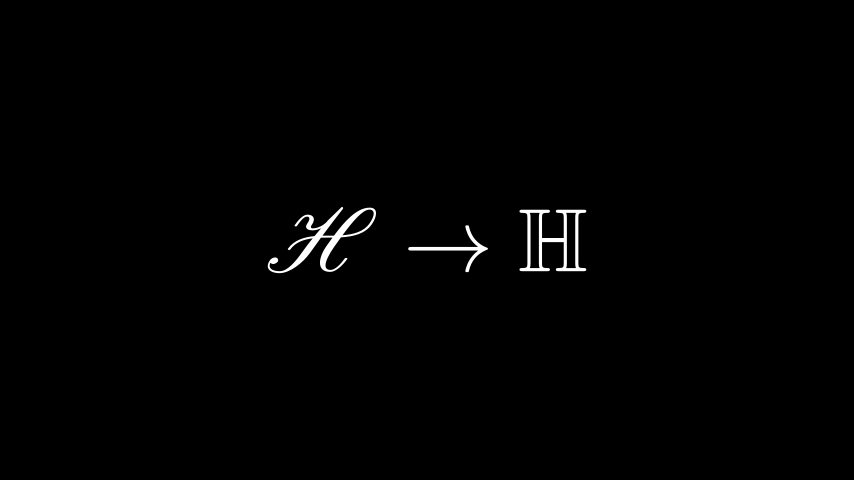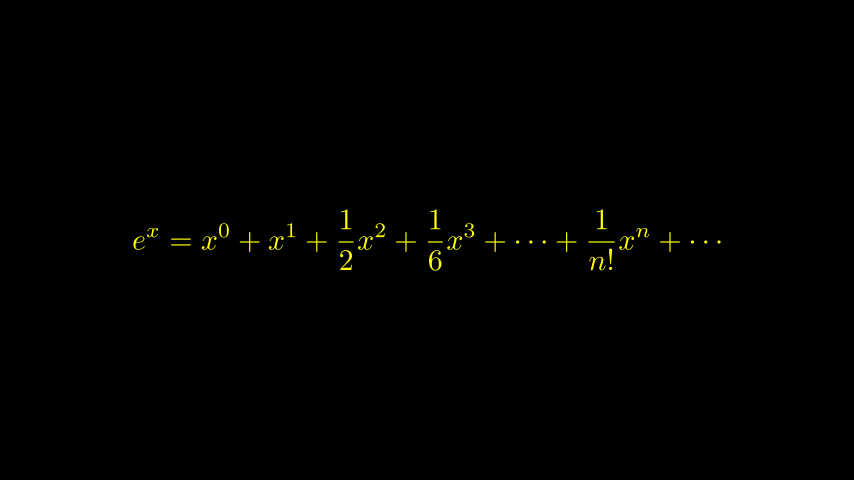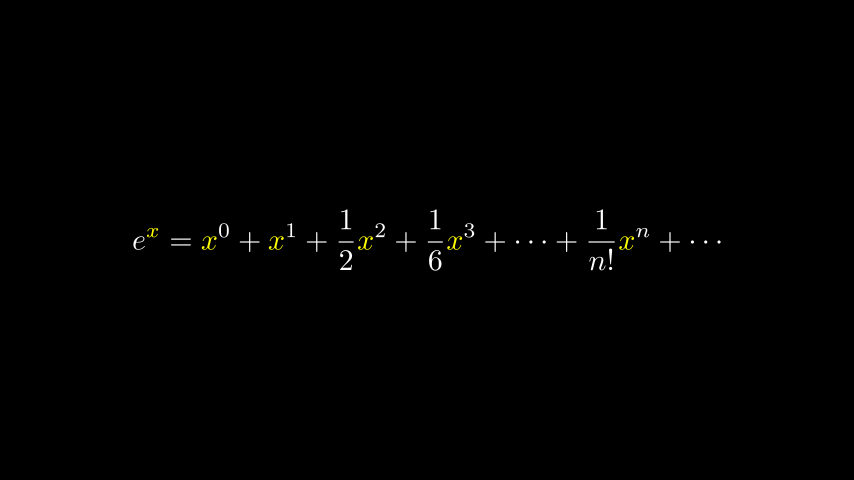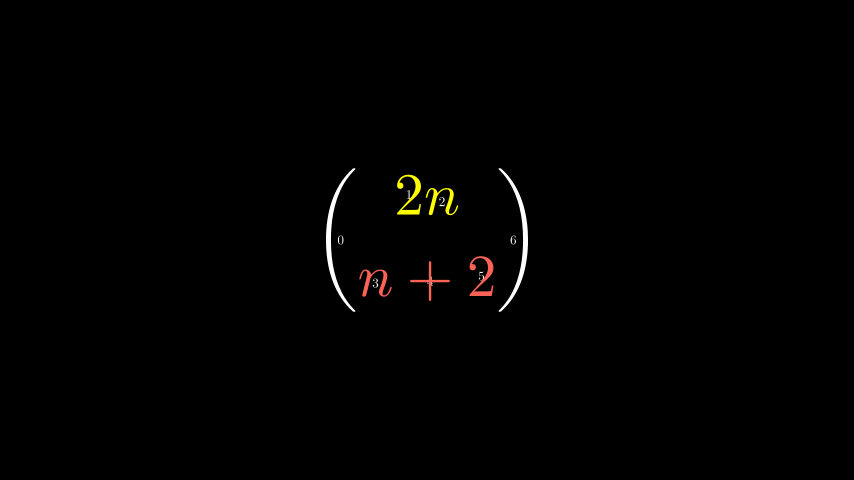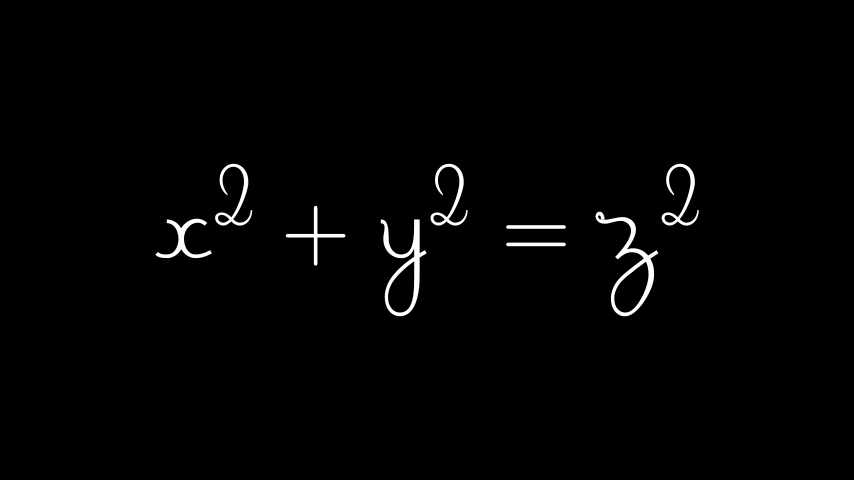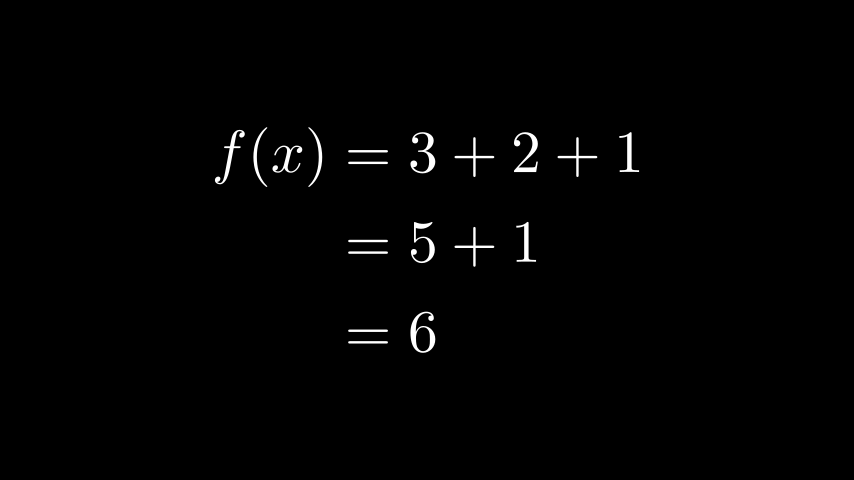渲染文本和公式
您可以通过两种不同的方式在视频中渲染 文本 :
使用 Pango ( text_mobject
使用 LaTeX ( tex_mobject
如果您想渲染简单的文本,您应该使用TextMarkupTextParagraph没有 LaTeX 的文本。
当你需要数学排版时应该使用 LaTeX。有关详细信息,请参阅 使用 LaTeX 编写文本。
没有 LaTeX 的文本
向动画添加文本的最简单方法是使用该类TextPango 库 来渲染文本。使用 Pango,您还可以渲染非英语字母,例如 hi 或 こんにちは 或 안녕하세요 或 Мрубя babæה。
这是一个简单的Hello World 动画。
示例:HelloWorld
Python from manim import *
class HelloWorld ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
text = Text ( "Hello world" , font_size = 144 )
self . add ( text )
参考:Text
您还可以使用MarkupTextMarkupText
示例:单线颜色
Python from manim import *
class SingleLineColor ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
text = MarkupText (
f 'all in red <span fgcolor=" { YELLOW } ">except this</span>' , color = RED
)
self . add ( text )
参考:MarkupText
与Text一起工作
本节介绍 的属性Text
使用字体
您可以使用 设置不同的字体font。
笔记
使用的字体必须安装在您的系统中,Pango 应该知道它。您可以使用 获取字体列表manimpango.list_fonts()。
Bash import manimpango
manimpango.list_fonts()
[ ...]
示例:字体示例
Python from manim import *
class FontsExample ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
ft = Text ( "Noto Sans" , font = "Noto Sans" )
self . add ( ft )
设置倾斜度和重量
Slant 是文本的样式,可以是NORMAL(默认), ITALIC或OBLIQUE。通常,对于许多字体来说,ITALIC和 OBLIQUE看起来很相似,但ITALIC使用Roman Style ,而 OBLIQUE使用Italic Style 。
粗细指定字体的粗细。您可以在 中看到权重列表 manimpango.Weight。
示例:Slants 示例
Python from manim import *
class SlantsExample ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
a = Text ( "Italic" , slant = ITALIC )
self . add ( a )
示例:不同的权重
Python from manim import *
class DifferentWeight ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
import manimpango
g = VGroup ()
weight_list = dict (
sorted (
{
weight : manimpango . Weight ( weight ) . value
for weight in manimpango . Weight
} . items (),
key = lambda x : x [ 1 ],
)
)
for weight in weight_list :
g += Text ( weight . name , weight = weight . name , font = "Open Sans" )
self . add ( g . arrange ( DOWN ) . scale ( 0.5 ))
使用颜色
您可以使用以下命令设置文本的颜色color:
示例:简单颜色
Python from manim import *
class SimpleColor ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
col = Text ( "RED COLOR" , color = RED )
self . add ( col )
您可以使用诸如t2c为特定字符着色之类的实用程序。如果您的文本包含连字(如迭代文本 中所述),这可能会出现问题。
t2c接受两种类型的词典,
键可以包含类似[2:-1]或 的索引,这与 Python 中的切片 [4:8]工作方式类似 。这些值应该是来自 的文本的颜色。Color
键包含应单独着色的单词或字符,值应为以下颜色Color:
示例:Textt2c 示例
Python from manim import *
class Textt2cExample ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
t2cindices = Text ( 'Hello' , t2c = { '[1:-1]' : BLUE }) . move_to ( LEFT )
t2cwords = Text ( 'World' , t2c = { 'rl' : RED }) . next_to ( t2cindices , RIGHT )
self . add ( t2cindices , t2cwords )
MarkupText.
使用渐变
您可以使用 添加渐变gradient。该值必须是任意长度的可迭代:
示例:渐变示例
Python from manim import *
class GradientExample ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
t = Text ( "Hello" , gradient = ( RED , BLUE , GREEN ), font_size = 96 )
self . add ( t )
t2g具有文本特定字符的渐变。它与颜色接口 具有类似的语法:
示例:t2g 示例
Python from manim import *
class t2gExample ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
t2gindices = Text (
'Hello' ,
t2g = {
'[1:-1]' : ( RED , GREEN ),
},
) . move_to ( LEFT )
t2gwords = Text (
'World' ,
t2g = {
'World' :( RED , BLUE ),
},
) . next_to ( t2gindices , RIGHT )
self . add ( t2gindices , t2gwords )
设置行距
您可以使用以下命令设置行间距line_spacing:
示例:行间距
Python from manim import *
class LineSpacing ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
a = Text ( "Hello \n World" , line_spacing = 1 )
b = Text ( "Hello \n World" , line_spacing = 4 )
self . add ( Group ( a , b ) . arrange ( LEFT , buff = 5 ))
禁用连字
通过禁用连字,您将获得字符和子对象之间的一对一映射。这解决了文本着色的问题。
警告
请注意,将此方法用于严重依赖连字(阿拉伯文本)的文本可能会产生意外结果。
您可以通过传递disable_ligatures到 来 禁用连字Text。例如:
示例:禁用连字
Python from manim import *
class DisableLigature ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
li = Text ( "fl ligature" , font_size = 96 )
nli = Text ( "fl ligature" , disable_ligatures = True , font_size = 96 )
self . add ( Group ( li , nli ) . arrange ( DOWN , buff = .8 ))
文本对象的行为类似于VGroups
例如,您可以通过迭代将每个字母设置为不同的颜色。
示例:迭代颜色
Python from manim import *
class IterateColor ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
text = Text ( "Colors" , font_size = 96 )
for letter in text :
letter . set_color ( random_bright_color ())
self . add ( text )
警告
请注意,连字 可能会在此处引起问题。如果您需要字符到子对象的一对一映射,您应该将参数传递disable_ligatures给Text禁用连字 。
与MarkupText一起工作
MarkupText 与 类似Text
MarkupText
示例:标记测试
Python from manim import *
class MarkupTest ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
text = MarkupText (
f '<span underline="double" underline_color="green">double green underline</span> in red text<span fgcolor=" { YELLOW } "> except this</span>' ,
color = RED ,
font_size = 34
)
self . add ( text )
使用 LaTeX 编写文本
正如您可以用来TextTex
例如,
示例:HelloLaTeX
Python from manim import *
class HelloLaTeX ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
tex = Tex ( r "\LaTeX" , font_size = 144 )
self . add ( tex )
笔记
请注意,我们使用原始字符串 ( r'...') 而不是常规字符串 ( '...')。这是因为 TeX 代码使用了很多特殊字符(例如\),这些字符在常规 Python 字符串中具有特殊含义。另一种方法是编写\\以避免反斜杠:Tex('\\LaTeX')。
与MathTex一起工作
默认情况下,传递到的所有内容都MathTexMathTexalign*环境中进行处理。Tex$符号 将公式括起来来实现类似的效果$\xrightarrow{x^6y^8}$::
示例:MathTeXDemo
Python from manim import *
class MathTeXDemo ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
rtarrow0 = MathTex ( r "\xrightarrow{x^6y^8}" , font_size = 96 )
rtarrow1 = Tex ( r "$\xrightarrow{x^6y^8}$" , font_size = 96 )
self . add ( VGroup ( rtarrow0 , rtarrow1 ) . arrange ( DOWN ))
LaTeX 命令和关键字参数
我们可以使用 AMS 数学包中的任何标准 LaTeX 命令。例如mathtt数学文本类型或looparrowright箭头。
示例:AMSLaTeX
Python from manim import *
class AMSLaTeX ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
tex = Tex ( r '$\mathtt {H} \looparrowright$ \LaTeX' , font_size = 144 )
self . add ( tex )
在 Manim 方面,该类TexTextcolor关键字更改 TeX mobject 的颜色。
示例:LaTeXAttributes
Python from manim import *
class LaTeXAttributes ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
tex = Tex ( r 'Hello \LaTeX' , color = BLUE , font_size = 144 )
self . add ( tex )
额外的 LaTeX 包
某些命令需要将特殊包加载到 TeX 模板中。例如,要使用mathscr脚本,我们需要添加mathrsfs 包。由于这个包默认没有加载到 Manim 的 tex 模板中,所以我们必须手动添加它。
示例:AddPackageLatex
Python from manim import *
class AddPackageLatex ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
myTemplate = TexTemplate ()
myTemplate . add_to_preamble ( r "\usepackage {mathrsfs} " )
tex = Tex (
r "$\mathscr {H} \rightarrow \mathbb {H} $}" ,
tex_template = myTemplate ,
font_size = 144 ,
)
self . add ( tex )
子串和部分
TeX mobject 可以接受多个字符串作为参数。tex[1]之后,您可以通过索引(如)或选择部分 tex 代码来引用各个部分。\bigstar在此示例中,我们设置使用的颜色set_color_by_tex():
示例:LaTeXSubstrings
Python from manim import *
class LaTeXSubstrings ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
tex = Tex ( 'Hello' , r '$\bigstar$' , r '\LaTeX' , font_size = 144 )
tex . set_color_by_tex ( 'igsta' , RED )
self . add ( tex )
请注意,set_color_by_tex()为包含 Tex 的整个子字符串着色,而不仅仅是特定符号或 Tex 表达式。考虑以下示例:
示例:不正确的 LaTeXSubstringColoring
Python from manim import *
class IncorrectLaTeXSubstringColoring ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
equation = MathTex (
r "e^x = x^0 + x^1 + \frac {1}{2} x^2 + \frac {1}{6} x^3 + \cdots + \frac {1} {n!} x^n + \cdots"
)
equation . set_color_by_tex ( "x" , YELLOW )
self . add ( equation )
正如您所看到的,这将整个方程染成黄色,这与预期相反。要仅着色为x黄色,我们必须执行以下操作:
示例:正确的 LaTeXSubstringColoring
Python from manim import *
class CorrectLaTeXSubstringColoring ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
equation = MathTex (
r "e^x = x^0 + x^1 + \frac {1}{2} x^2 + \frac {1}{6} x^3 + \cdots + \frac {1} {n!} x^n + \cdots" ,
substrings_to_isolate = "x"
)
equation . set_color_by_tex ( "x" , YELLOW )
self . add ( equation )
通过设置substrings_to_isolate,x我们会自动将 拆分 MathTexx组件隔离为单独的子字符串。只有这样才能set_color_by_tex()达到预期的效果。
请注意,Manim 还支持自定义语法,可以轻松地将 TeX 字符串拆分为子字符串:只需用双括号将要隔离的公式部分括起来即可。在 string 中 ,渲染的 mobject 将由子字符串, , , , 和组成。这使得使用 可以轻松编写相似文本片段之间的转换。MathTex(r"{{ a^2 }} + {{ b^2 }} = {{ c^2 }}")``a^2``+``b^2``=``c^2TransformMatchingTex
用于index_labels处理复杂的字符串
有时您可能会使用非常复杂的MathTexindex_labels()
该方法显示 mobject 的子 mobject 的索引,使您可以轻松找到要更改的 mobject 的组件。
示例:IndexLabelsMathTex
Python from manim import *
class IndexLabelsMathTex ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
text = MathTex ( r "\binom {2n} {n+2}" , font_size = 96 )
# index the first (and only) term of the MathTex mob
self . add ( index_labels ( text [ 0 ]))
text [ 0 ][ 1 : 3 ] . set_color ( YELLOW )
text [ 0 ][ 3 : 6 ] . set_color ( RED )
self . add ( text )
LaTeX 数学字体 - 模板库
在排版数学公式时更改 LaTeX 中的字体比常规文本更棘手。它需要更改用于编译 TeX 的模板。Manim 附带了一系列TexFontTemplates
示例:LaTeXMathFonts
Python from manim import *
class LaTeXMathFonts ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
tex = Tex (
r "$x^2 + y^2 = z^2$" ,
tex_template = TexFontTemplates . french_cursive ,
font_size = 144 ,
)
self . add ( tex )
Manim 还包含TexTemplateLibraryTexText
示例:LaTeXTemplateLibrary
Python from manim import *
class LaTeXTemplateLibrary ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
tex = Tex ( 'Hello 你好 \\ LaTeX' , tex_template = TexTemplateLibrary . ctex , font_size = 144 )
self . add ( tex )
对齐公式
MathTexalign* 。这意味着您可以在排版多行公式时使用&对齐字符:
示例:LaTeXAlignEnvironment
Python from manim import *
class LaTeXAlignEnvironment ( Scene ):
def construct ( self ):
tex = MathTex ( r 'f(x) &= 3 + 2 + 1 \\ &= 5 + 1 \\ &= 6' , font_size = 96 )
self . add ( tex )